Hey everybody, I’m Richard Jant, and today I’m going to walk you through a shoe factory. We will visit a shoes factory to see how shoes are made.Let’s check it out, okay?
So, what we have here is Chinese shoe factory with 40 years history. This is all the componentry that you would need to basically make a pair of shoes. We’ll go through department by department, and you can see now, this shoe factory, like this, depending on the complexity of the shoe, could make between 1500 and 3000 pairs a day.
How Shoes Are Made?
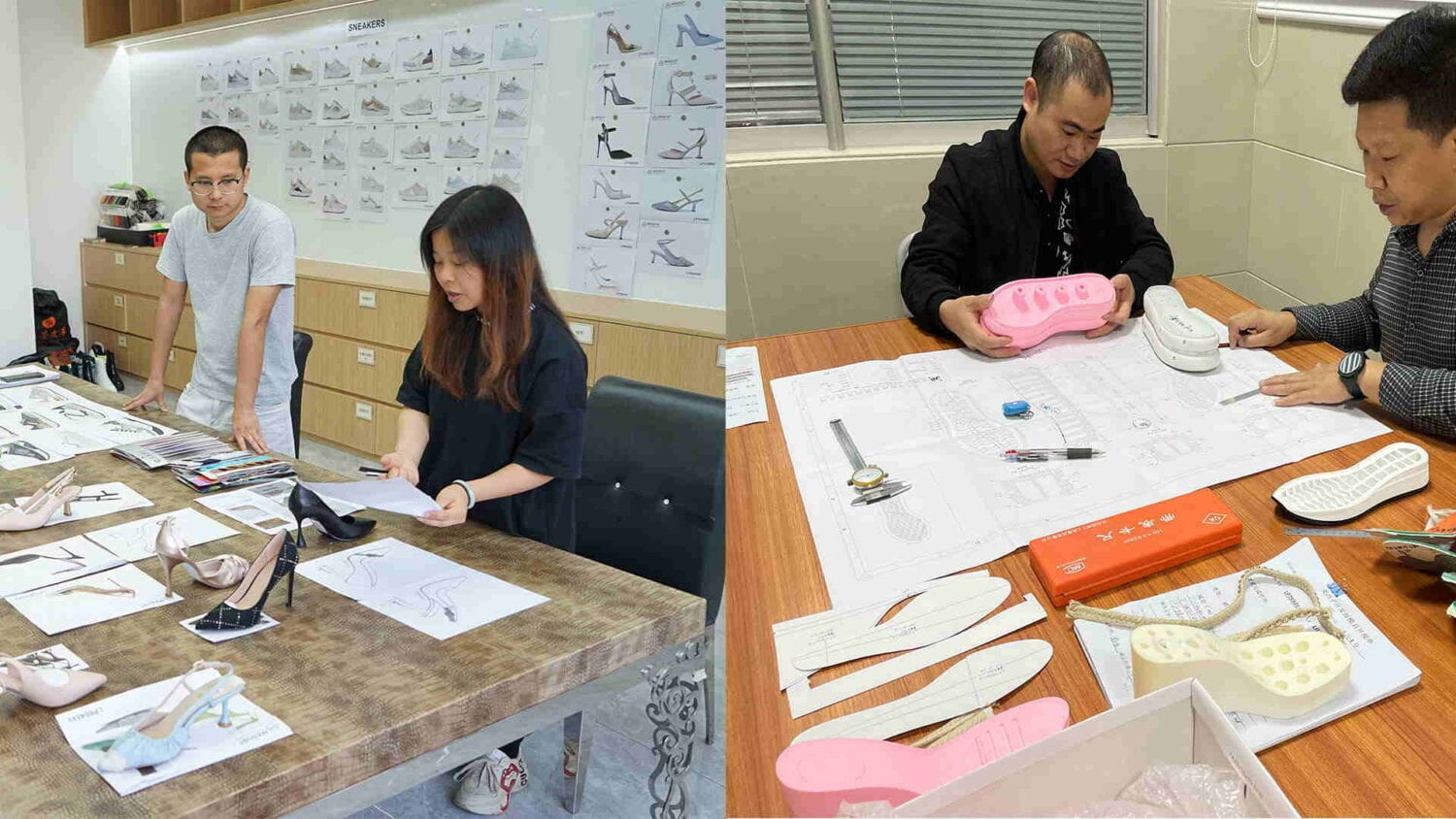
Now, let’s get a look. The first thing you have is the management office. So what goes on in the management office? You’ve got the owner of the factory, the manager, and also the business manager. These are the people that do the buying, scheduling, and the footwear developers may also be in this area. But this is all the backroom operation stuff because anything that you put into a shoe has to be bought, so that has to be scheduled and delivered. These people basically control all that stuff.
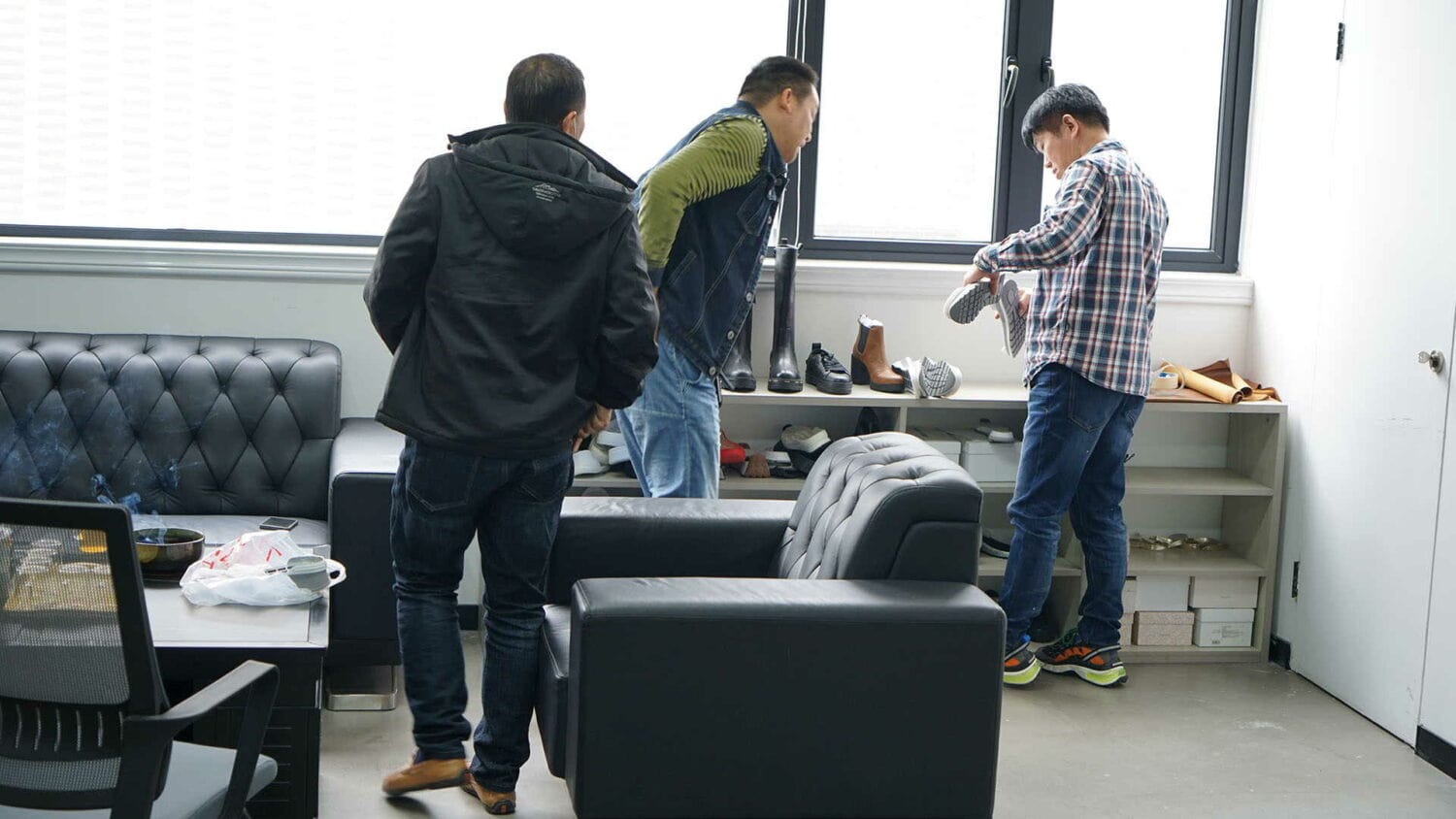

The development room is next. In the development room, this is where, when you send your design, this is where it lands first. This is where the skilled stitchers, the sample cutters, and the pattern maker work. These are the most experienced stitchers, the pattern cutters, and they have enough equipment to essentially hand make your test pattern shoe for you.
That’s where your product development starts. You meet with the factory boss and you send it over to the sample development room. So most of the work in the development process is going on here in the sample development room.

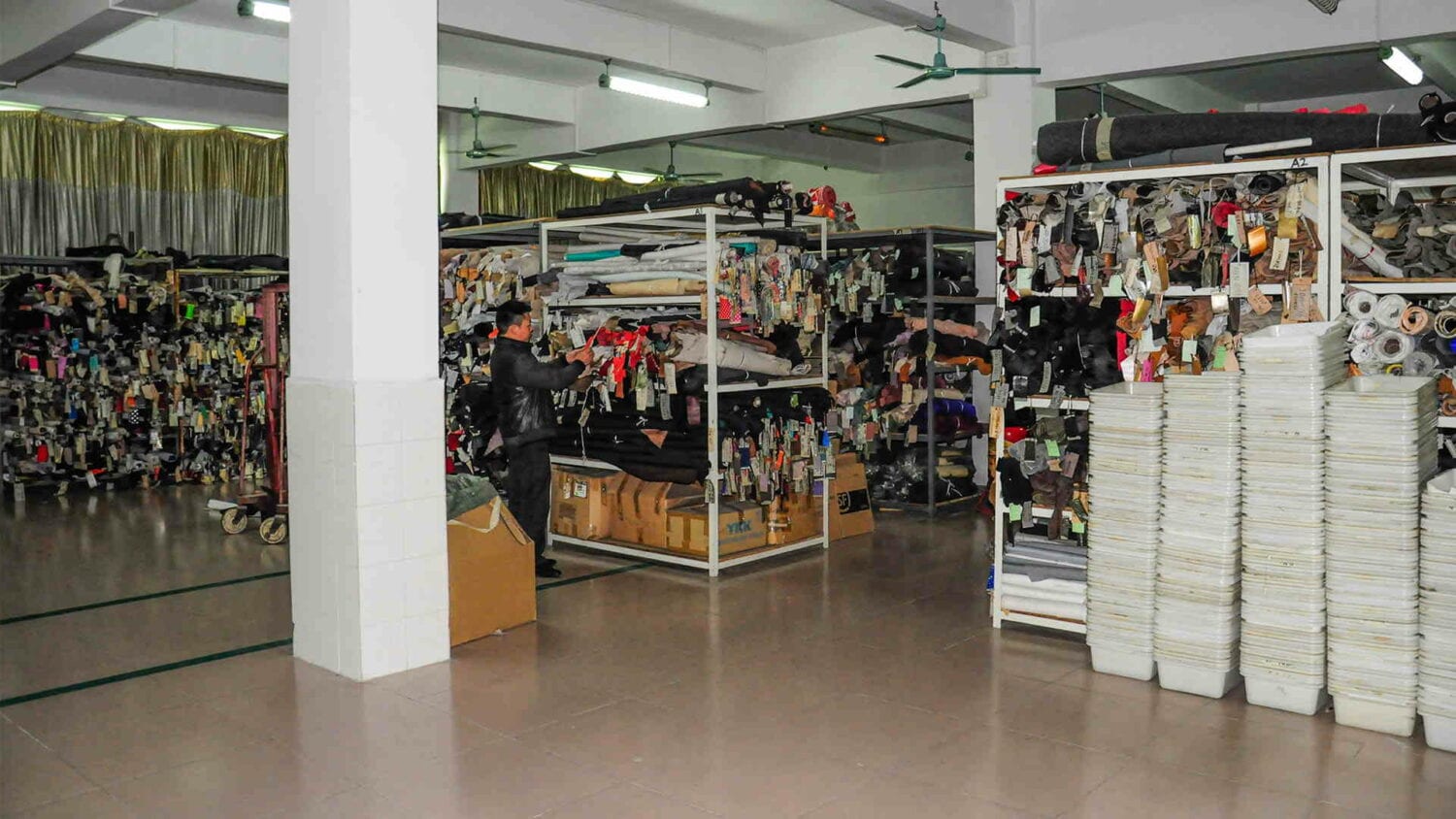
Now, let’s go on to what happens when a shoe goes into production. Basically, the business office is going to order the materials, and all those materials are going to show up in the warehouse. In this warehouse, you have literally everything you need to make a shoe. You have the leather, the textile, the rubber, the outsole components, if they’re made in another factory, have to get put into the warehouse. You’re also going to have the last and the cutting dies.
Of course, when raw materials come in or outsoles or whatever, everything has to get inspected. So there’s a big QC operation going on here inside the material warehouse.

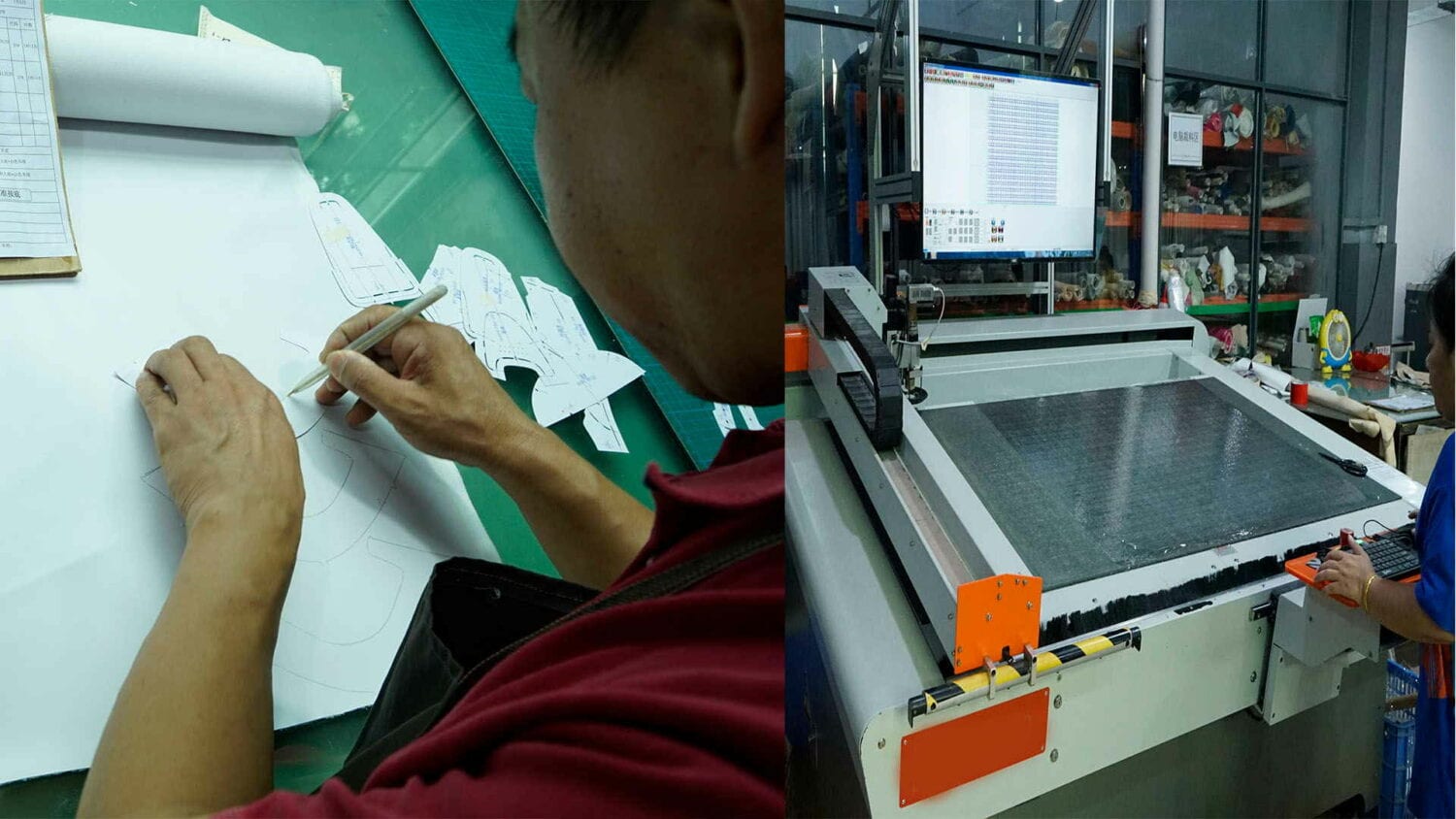
Now, the orders come in, and the first thing that’s going to happen is materials are going to go to the cutting department. This is where leather, mesh, textile, anything that has to be cut is going to get processed. The workers here will have different kinds of cutting machines, whether it’s leather, textile, fabric, or even water jet if it’s sophisticated. These are what manual presses look like, but again, you’ll have the cutting, and then behind each cutter, you’ll see over here that they have a stacker.
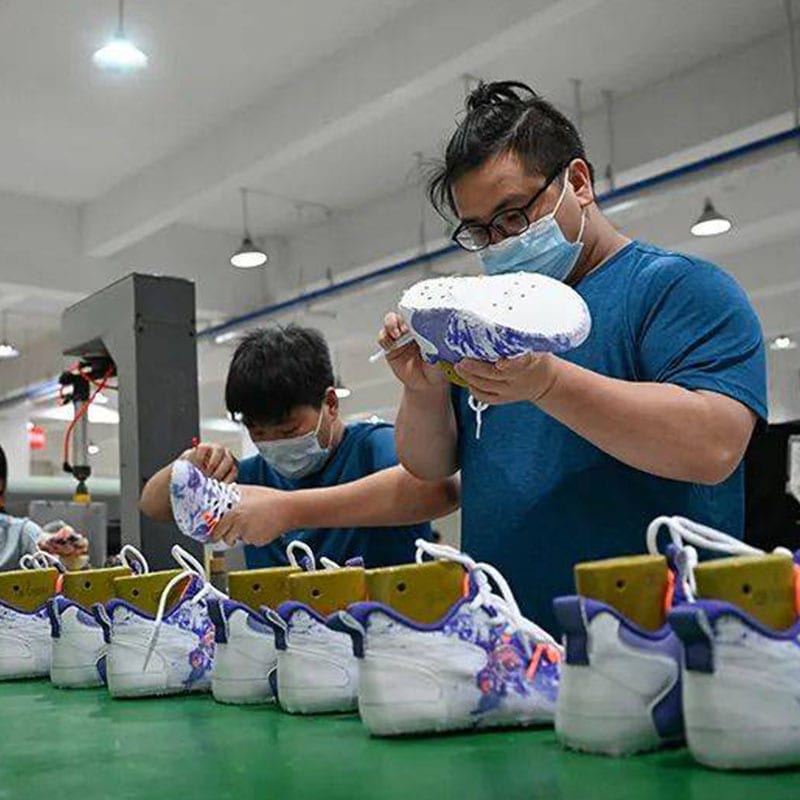
Let’s get back over here to the cutting department. The cutter will be operating the cutting machine, and there’ll be a worker right next to him or her that basically collects all the pieces and stacks them to keep the pieces organized. Because if you imagine, if you’re cutting a complicated shoe that could have 20 parts and you’re going to cut 10,000 worth, that’s a lot of parts, and if they’re all different sizes and they don’t have the size marking on it, it’s really complicated really quickly.

That’s the cutting department. Once the cutting department is done, all those upper components have to get processed. Anything that has a logo on it or needs a stitching guide or needs edges skived so they can be rolled over, all that processing has to be done in the prep department. So the prep department is going to again prepare the pieces right, so anything that has a logo on it or has to be skived or whatever, they have to do all that processing before the cutting team could get at it.
Now, this group also will put together kits. That’ll take all those pieces and gather them all together so that you can hand that bag of components to the stitcher, and they can do it. Now, once you get into the stitching department, generally to support one stitching line, you’re going to have hundreds of stitches. This is not many. You’ll have 10 times as many managers to really make a big stitching line for a small, simple shoe.
Yeah, there could be electronic stitching equipment also without humans or if it’s a knit upper, then you don’t need so many stitches. But these folks do all the stitching operations, and they divide the work up. Someone stitcher doesn’t take all the components and put it together. That one stitcher basically does one operation and passes it off to the next person.
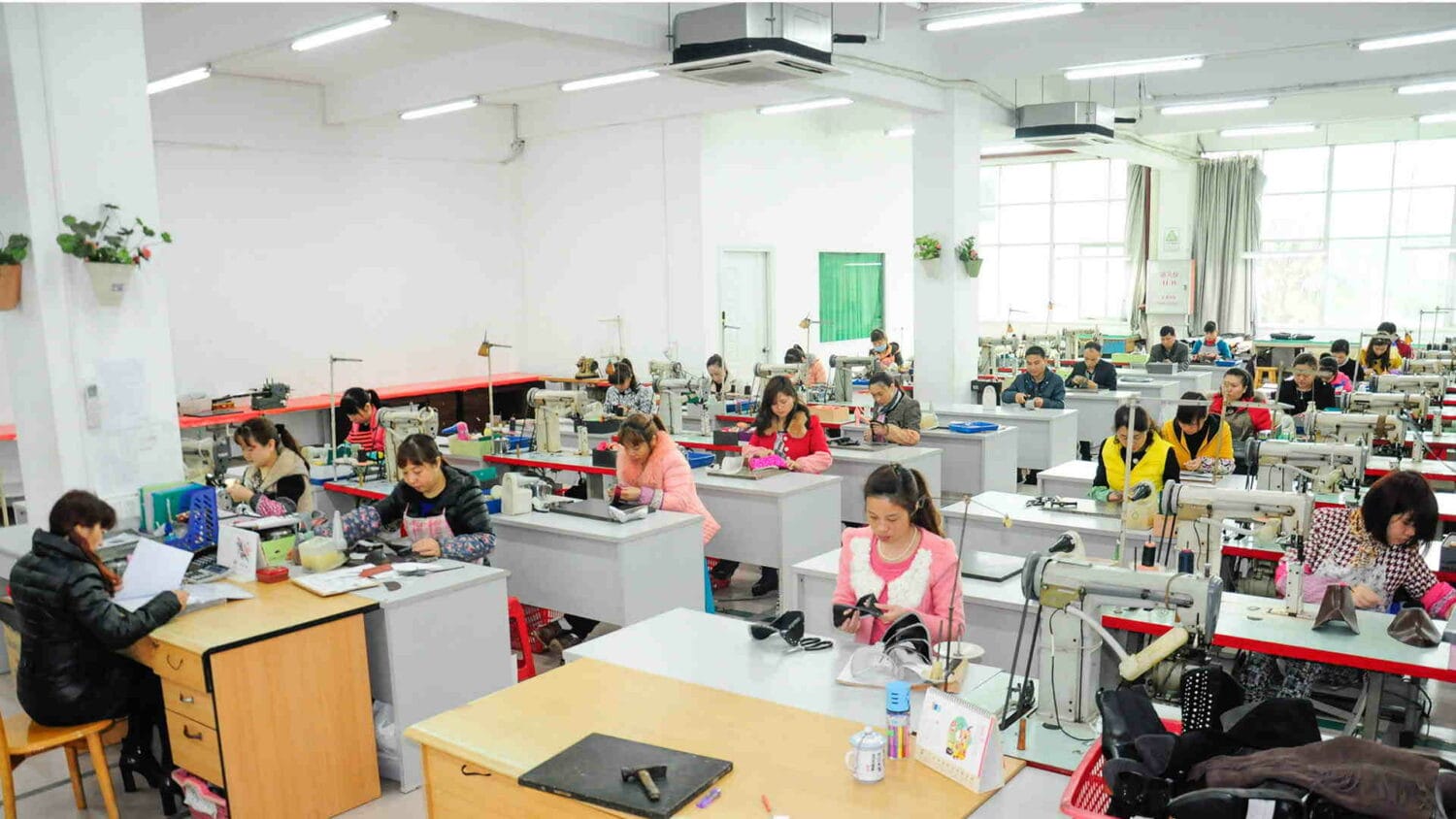

Just like in all the other departments, there’s quality control. Once the stitching operations are done, you have to have a team of people check it, and there are some other operations that you do during the stitching operation before you put the bottom on. If it’s an athletic shoe, you’re going to set the toe puff or you’re going to mold the heel counter. Those things get done.
Now, while that’s getting done, the outsole components are going to be over here. These are going to be the stock fitting operation. So if you have a multi-part outsole, say it’s a capsule that has EVA inside or if it’s molded EVA and has an injection piece, all those parts have to get glued together before everything goes to the main assembly line. So that’s what stock fitting is.
Here, the workers are unboxing the parts. They’ve already been inspected in the warehouse. They’re unboxing the parts, and they’re going to put glue and primer, and there’ll be a pressing operation. They’ll get all those pieces checked out and basically get the sole units finished so that the sole can meet the upper.
Let’s get on to that because all this stuff happens in the background because you need to feed the assembly line. You don’t want to mess around and have the assembly line waiting. So you get all this stuff done, and either it’s in the warehouse waiting or it’s a just-in-time assembly line where it goes right from one machine to the next. You have to organize it so that nobody’s waiting because that’s not efficient.
Let’s get down here to the front of the assembly line. The first thing that happens at the front of the assembly line, we say assembly line, but really, what we’re talking about is gluing the upper and the bottom together. The first thing that happens is the shoe last gets inserted into the upper, whether it’s a strobel or whether it’s a board last. That’s a very first operation. If it’s a strobel shoe, they might steam the upper and then shoehorn the upper onto the last. If it’s board lasting, they’re going to basically heat up the upper, get a little glue on the strobel board, and then they’re going to use a board lasting machine like this.
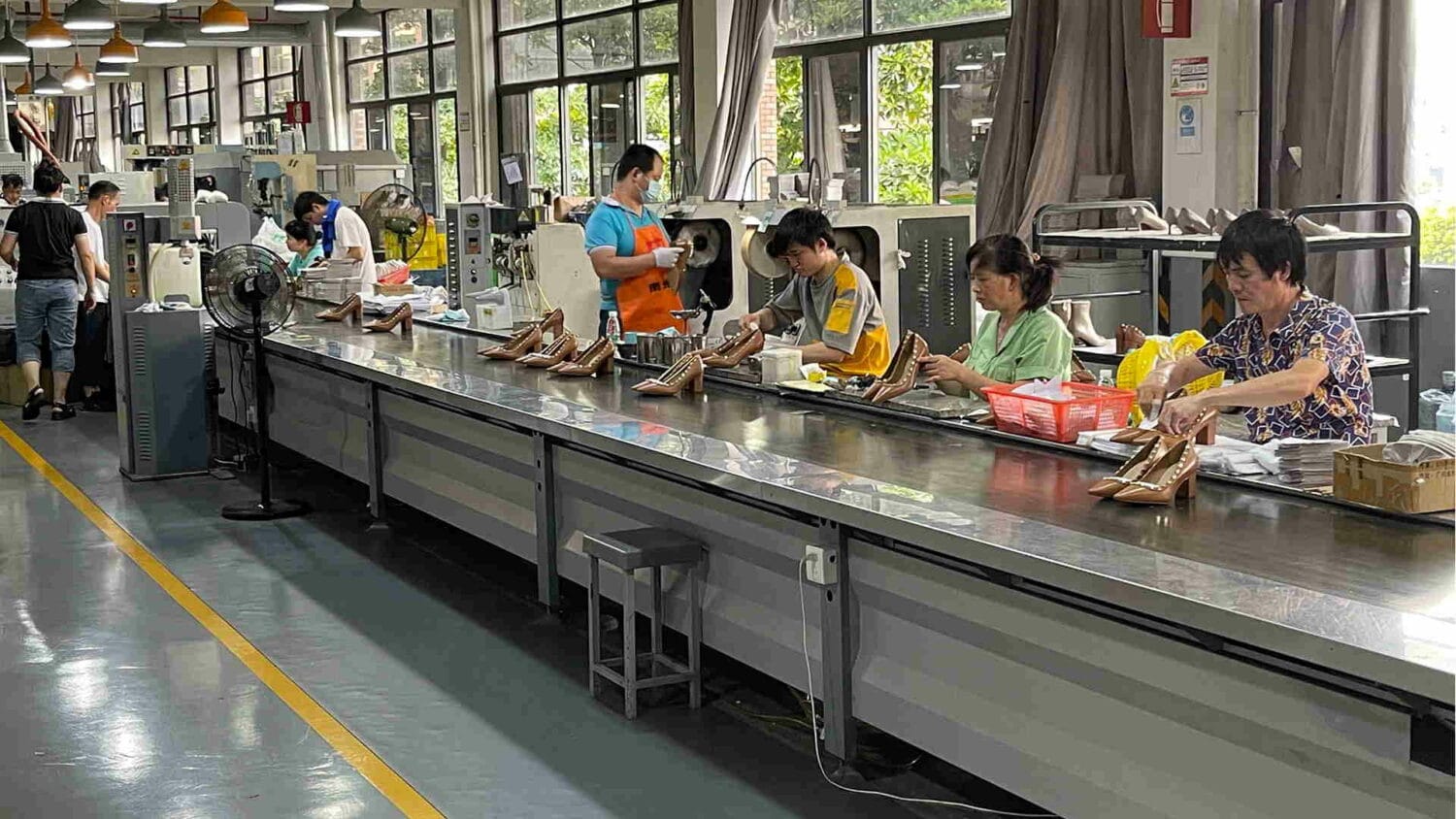

Once you do some board lasting, you might do some waist lasting or toe puff setting or heel setting. Basically, get that upper onto the last nice and tight so you can glue the bottom on. If there’s a little wrinkle left after toe lasting, then there’ll be a buffing station. And the assembly line, this conveyor belt runs through all the middle of this, so you do your operation and you put it back on the assembly line.
The next thing is the workers are going to start applying primer and cement. Primer basically gets the upper surface and the outsole surface ready to be glued together. So a primer is generally glue mixed with a solvent or it could be water-based.
Now, when you get down here, the worker is basically going to put those two pieces together, and they fit them together by hand. There’s a human being that’s lining the two pieces up and pushing them together. Once it’s fit together, it’ll go to a pressing machine. That’s the operation here, where a hydraulic press basically squeezes down on the upper of the last and outsole to make sure they all fit together. Make sure there are no air bubbles or air gaps or anything like that.
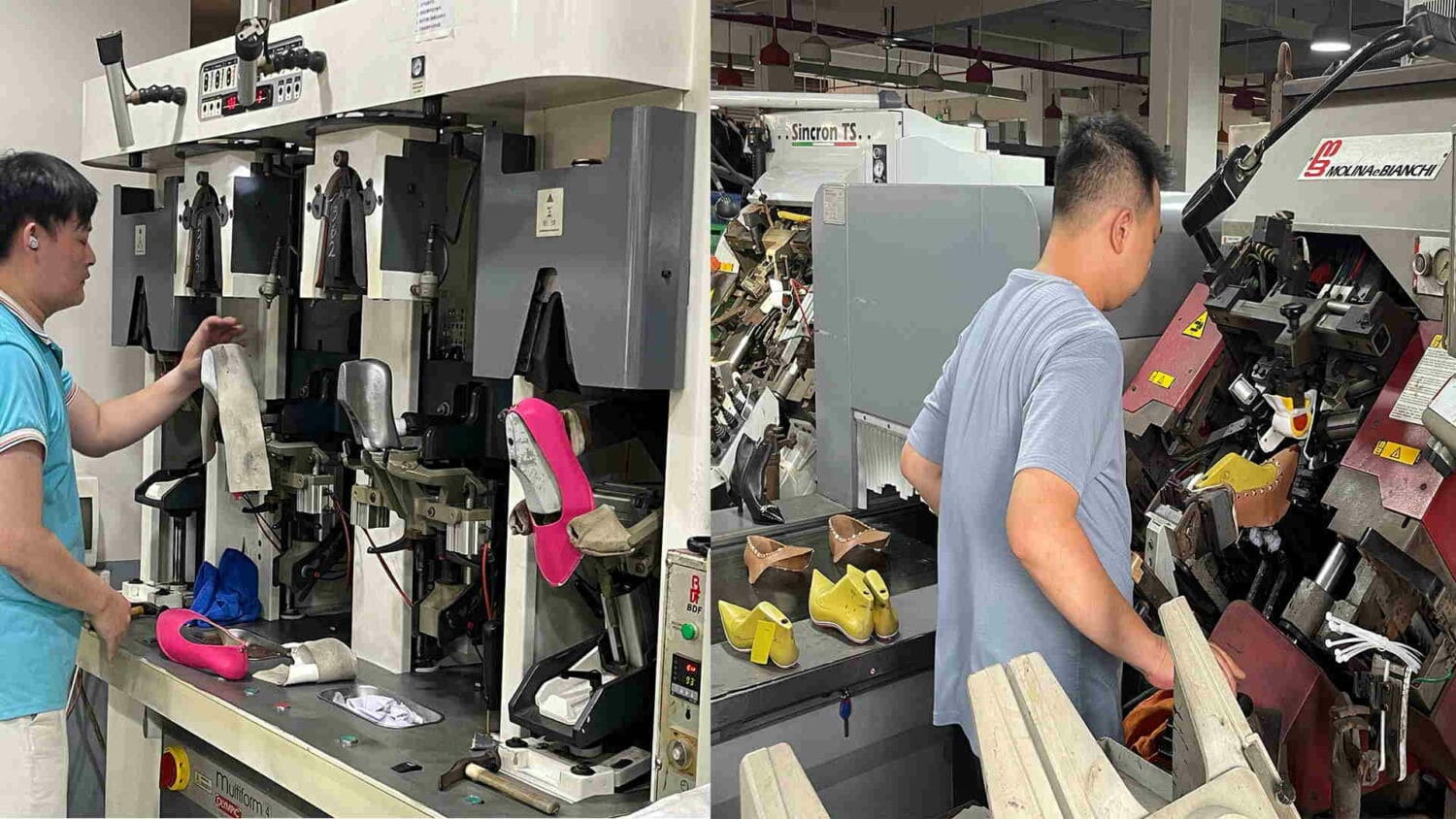

Next, it’ll go into a chiller. The chilling machine basically sets the glue. The next operation is de-lasting. If you’ve ever tried to pull a last out of a shoe, it’s difficult. I mean, if you do it yourself, okay, fine, you can take two minutes to do it. They actually will have a machine do that because you want to make sure to do it quickly but also not damage the shoe.
Again, that’s actually primed for all of this stuff. Is you want to be careful that in the assembly operation, whether you’re pressing or de-lasting, that you don’t actually damage the shoe while you’re trying to make it. I know it sounds crazy, but it happens.
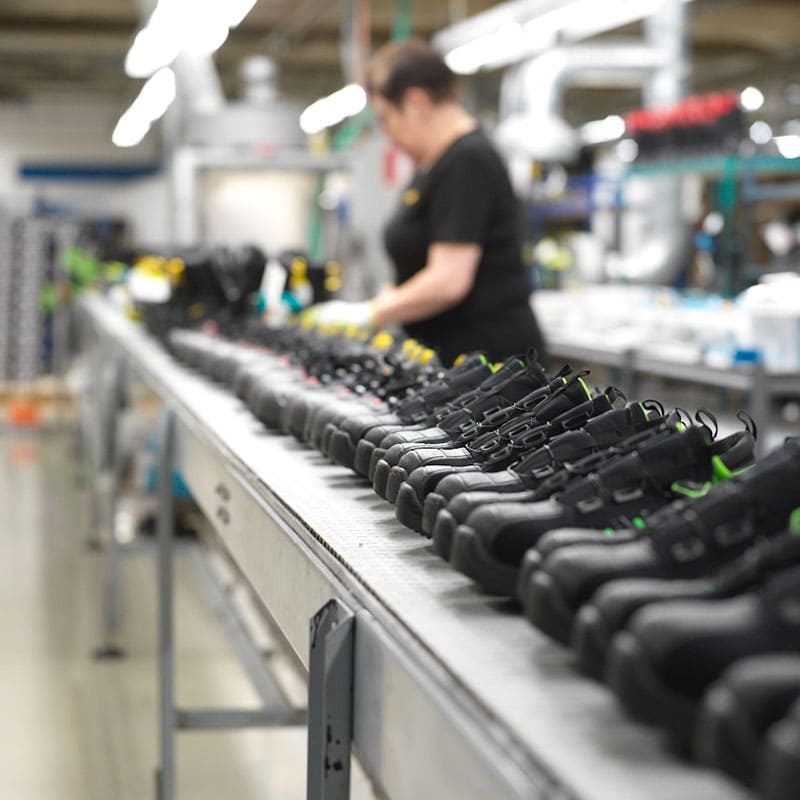
Okay, next thing is once you’ve got the last out, it’s time to put the shoelace in and put some stuffing paper in. Also, there’ll be a QC station. So you’ll have this at the end of the assembly line. All the workers will be checking the shoe, putting it in the box and the label, making sure you’ve got a pair, making sure they’re the right size, and getting them into the box. Make sure everything’s clean. So here you have a QC manager, and they’ll be checking the case packing. The last thing they’ll do is they’ll run these into a warehouse or they’ll just load them directly into a container. So there’s the container loading.

That’s basically how shoes are made. Now, it takes us 10 minutes to discuss this operation, but it’ll take a little while to get through this by the time you go from the warehouse to the cutting to the stock fitting and the scheduling operations to make sure it all happens together. That’s a real challenge, and it doesn’t happen all in one day. You might spend a day or two in cutting because you’re doing a lot of processing, but that’s basically how the operation works.
A factory like this might have 200 to 500 people, depending on the complexity of a shoe. A micro factory may have just a hundred people, depending on the complexity of the issue. Really, it’s the stitching that drives it. So that’s the really interesting challenge where you’ll walk into a shoe factory that could be as big as a city, but the building block is essentially set up like this.
Again, this is basically that unit so that you have built capacity to support what goes on in the assembly line. In a big tall UGG snowboard boot, maybe it’s just 600 or 700 a day. A women pumps, you can maybe make 2000 a day because it’s such a simple shoe.
Anyways, hey folks, that’s how shoes are made in the shoe factory. If you’re interested in starting a shoe business and you want to talk to experts, Please contact us. If you are looking for a private label shoe manufacturer to produce shoes for you, you can read my previous article which is very useful. Please click here to view it: 8 Tips to Quickly Identify a Good Shoe Supplier